Linux如何用脚本查看系统信息-创新互联
Linux如何用脚本查看系统信息?这篇文章运用了实例代码展示,代码非常详细,可供感兴趣的小伙伴们参考借鉴,希望对大家有所帮助。

#!/bin/bash
# auth:Bertram
# created Time : 2019-12-26
# func:sys info check
# sys:centos6.x/7.x
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ $(id -u) -ne 0 ] && echo "请用root用户执行此脚本!" && exit 1
sysversion=$(rpm -q centos-release|cut -d- -f3)
line="-------------------------------------------------"
[ -d logs ] || mkdir logs
#sys_check_file="logs/$(ip a show dev eth0|grep -w inet|awk '{print $2}'|awk -F '/' '{print $1}')-`date +%Y%m%d`.txt"
sys_check_file="logs/$(ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}')-`date +%Y%m%d`.txt"
# 获取系统cpu信息
function get_cpu_info() {
Physical_CPUs=$(grep "physical id" /proc/cpuinfo| sort | uniq | wc -l)
Virt_CPUs=$(grep "processor" /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l)
CPU_Kernels=$(grep "cores" /proc/cpuinfo|uniq| awk -F ': ' '{print $2}')
CPU_Type=$(grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sort | uniq)
CPU_Arch=$(uname -m)
#echo -e '\033[32m CPU信息:\033[0m'
echo -e '\033[05;32m CPU信息:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF | column -t
物理CPU个数: $Physical_CPUs
逻辑CPU个数: $Virt_CPUs
每CPU核心数: $CPU_Kernels
CPU型号: $CPU_Type
CPU架构: $CPU_Arch
EOF
}
# 获取系统内存信息
function get_mem_info() {
Total=$(free -m | sed -n '2p' | awk '{print $2"M"}')
Used=$(free -m | sed -n '2p' | awk '{print $3"M"}')
Rate=$(free -m | sed -n '2p' | awk '{print""($3/$2)*100"%"}')
echo -e '\033[05;31m 内存信息:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF | column -t
内存总容量:$Total
内存已使用:$Used
内存使用率:$Rate
EOF
}
# 获取系统网络信息
function get_net_info() {
pri_ipadd=$(ifconfig |awk 'NR==2{print $2}')
#pub_ipadd=$(curl ip.sb 2>&1)
pub_ipadd=$(curl -s http://ddns.oray.com/checkip | awk -F ":" '{print $2}' | awk -F "<" '{print $1}'|awk '{print $1}')
gateway=$(ip route | grep default | awk '{print $3}')
mac_info=$(ip link| egrep -v "lo"|grep link|awk '{print $2}')
dns_config=$(egrep 'nameserver' /etc/resolv.conf)
route_info=$(route -n)
echo -e '\033[05;33m IP信息:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF | column -t
系统公网地址: ${pub_ipadd}
系统私网地址: ${pri_ipadd}
网关地址: ${gateway}
MAC地址: ${mac_info}
路由信息:
${route_info}
DNS 信息:
${dns_config}
EOF
}
# 获取系统磁盘信息
function get_disk_info() {
disk_info=$(fdisk -l|grep "Disk /dev"|cut -d, -f1)
disk_use=$(df -hTP|awk '$2!="tmpfs"{print}')
disk_inode=$(df -hiP|awk '$1!="tmpfs"{print}')
echo -e '\033[05;34m 磁盘信息:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF
${disk_info}
磁盘使用:
${disk_use}
inode信息:
${disk_inode}
EOF
}
# 获取系统信息
function get_systatus_info() {
sys_os=$(uname -o)
sys_release=$(cat /etc/redhat-release)
sys_kernel=$(uname -r)
sys_hostname=$(hostname)
sys_selinux=$(getenforce)
sys_lang=$(echo $LANG)
sys_lastreboot=$(who -b | awk '{print $3,$4}')
sys_runtime=$(uptime |awk '{print $3,$4}'|cut -d, -f1)
sys_time=$(date)
sys_load=$(uptime |cut -d: -f5)
echo -e '\033[05;35m 系统信息:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF | column -t
系统: ${sys_os}
发行版本: ${sys_release}
系统内核: ${sys_kernel}
主机名: ${sys_hostname}
selinux状态: ${sys_selinux}
系统语言: ${sys_lang}
系统当前时间: ${sys_time}
系统最后重启时间: ${sys_lastreboot}
系统运行时间: ${sys_runtime}
系统负载: ${sys_load}
EOF
}
# 获取服务信息
function get_service_info() {
port_listen=$(netstat -lntup|grep -v "Active Internet")
kernel_config=$(sysctl -p 2>/dev/null)
if [ ${sysversion} -gt 6 ];then
service_config=$(systemctl list-unit-files --type=service --state=enabled|grep "enabled")
run_service=$(systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running |grep ".service")
else
service_config=$(/sbin/chkconfig | grep -E ":on|:启用" |column -t)
run_service=$(/sbin/service --status-all|grep -E "running")
fi
echo -e '\033[05;36m 服务启动配置:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF
${service_config}
${line}
运行的服务:
${run_service}
${line}
监听端口:
${port_listen}
${line}
内核参考配置:
${kernel_config}
EOF
}
function get_sys_user() {
login_user=$(awk -F: '{if ($NF=="/bin/bash") print $0}' /etc/passwd)
ssh_config=$(egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config)
sudo_config=$(egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/sudoers |grep -v "^Defaults")
host_config=$(egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/hosts)
crond_config=$(for cronuser in /var/spool/cron/* ;do ls ${cronuser} 2>/dev/null|cut -d/ -f5;egrep -v "^$|^#" ${cronuser} 2>/dev/null;echo "";done)
echo -e '\033[05;37m 系统登录用户:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF
${login_user}
${line}
ssh 配置信息:
${ssh_config}
${line}
sudo 配置用户:
${sudo_config}
${line}
定时任务配置:
${crond_config}
${line}
hosts 信息:
${host_config}
EOF
}
function process_top_info() {
top_title=$(top -b n1|head -7|tail -1)
cpu_top10=$(top b -n1 | head -17 | tail -10)
mem_top10=$(top -b n1|head -17|tail -10|sort -k10 -r)
echo -e '\033[05;38m CPU占用top10:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF
${top_title}
${cpu_top10}
EOF
echo -e '\033[05;39m 内存占用top10:\033[0m'
cat <<EOF
${top_title}
${mem_top10}
EOF
}
function sys_check() {
get_cpu_info
echo ${line}
get_mem_info
echo ${line}
get_net_info
echo ${line}
get_disk_info
echo ${line}
get_systatus_info
echo ${line}
get_service_info
echo ${line}
get_sys_user
echo ${line}
process_top_info
}
sys_check > ${sys_check_file}结果如图 :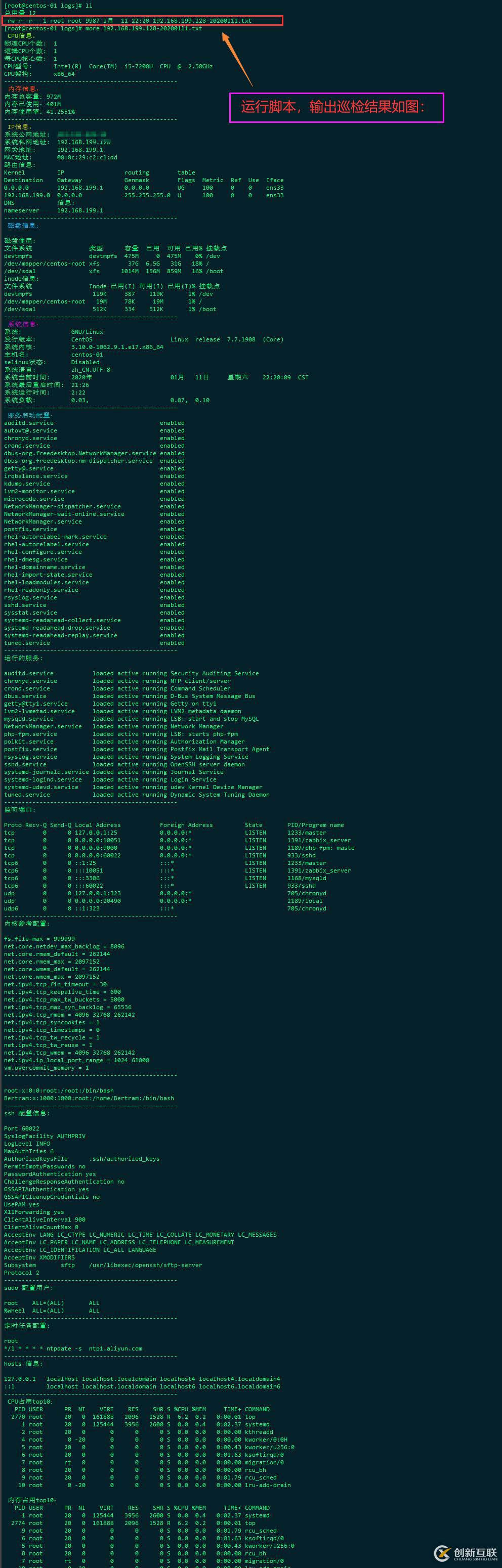
关于用脚本查看Linux系统信息的脚本就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
另外有需要云服务器可以了解下创新互联cdcxhl.cn,海内外云服务器15元起步,三天无理由+7*72小时售后在线,公司持有idc许可证,提供“云服务器、裸金属服务器、高防服务器、香港服务器、美国服务器、虚拟主机、免备案服务器”等云主机租用服务以及企业上云的综合解决方案,具有“安全稳定、简单易用、服务可用性高、性价比高”等特点与优势,专为企业上云打造定制,能够满足用户丰富、多元化的应用场景需求。
新闻名称:Linux如何用脚本查看系统信息-创新互联
网页网址:https://www.cdcxhl.com/article26/dochcg.html
成都网站建设公司_创新互联,为您提供自适应网站、商城网站、网站收录、网站策划、定制开发、网站制作
声明:本网站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以用户投稿、用户转载内容为主,如果涉及侵权请尽快告知,我们将会在第一时间删除。文章观点不代表本网站立场,如需处理请联系客服。电话:028-86922220;邮箱:631063699@qq.com。内容未经允许不得转载,或转载时需注明来源: 创新互联

- 网站排名波动大的原因 2023-03-30
- 深圳网站制作谈网站排名的难易 2022-05-27
- 提高网站排名的几个因素 2013-10-24
- 成都市网站建设:如何让你的网站排名比较好 2022-09-30
- 中小企业如何优化网站排名进行营销? 2016-11-27
- 解析锚文本对网站排名的作用 2021-11-04
- SEOEer新手应当如何对网站排名进行分析? 2023-04-14
- 威海网站排名要害词优化排名为什么这么重要? 2023-01-08
- 制作网站怎么提前进行网站排名优化 2020-11-28
- 如何闯过优化关卡才能提升网站排名 2022-09-30
- 怎么才能让网站排名逐渐上升呢?有哪些技巧 2022-12-13
- SEO优化之网站排名不保证和提升问题 2022-03-15